Gram Stain – Semen:
Why Gram Stain (Semen) Test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
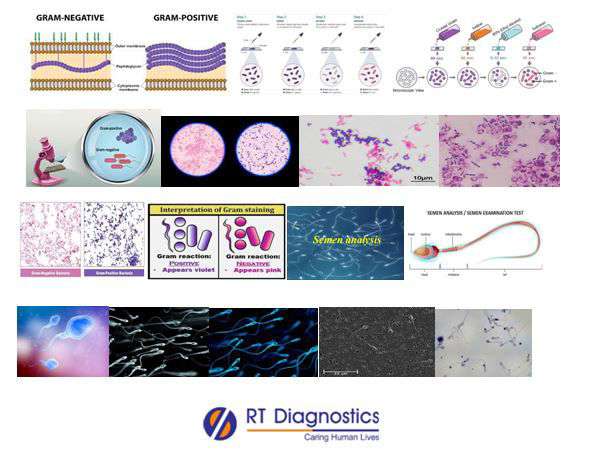
Semen is a complex substance produced by the male reproductive organs. It is a greyish white or yellowish tint body fluid secreted by the gonads (sexual gland of the male). Semen is also called the seminal fluid that is mainly composed of water, plasma, mucus, citric acid, lipids, sperm/spermatozoa, proteins, fructose, essential nutrients eg. sodium, potassium, zinc, chlorine, magnesium, phosphorous, vitamin B12 uric acid, lactate, enzymes (proteolytic enzymes) like acid phosphatase etc, blood group antigens and other nutrients that will help the sperm to survive to facilitate successful fertilization. This microbial pathogen test in semen culture is performed in certain suspected patients with clinical manifestations of infection and/or inflammation and also infertility related issues in males eg. IVF etc. Other tests include complete semen analysis that measures liquid portion called seminal fluid and the microscopic part i.e moving cells called sperms, number of WBCs (indicating infection etc). The assessment includes evaluation of the physical and chemical properties of human semen like pH, viscosity, osmolarity, coagulation and liquefaction, buffering capacity and also includes the estimation of qualitative (eg. normal morphology, number of immature sperms, motility etc) & quantitative analysis (eg. volume like sperm density etc) of the specimen. Factors that can affect the sperm count or semen analysis values include alcohol, tobacco, caffeine, medications such as cimetidine etc. Culture and Sensitivity test for microbial growth in semen specimen test helps arrive at a definitive diagnosis thereby ruling out other similar possibilities of pathology causing such similar clinical manifestations. Semen test helps to detect DNA damage test (detection of DNA fragmentation by TUNEL assay) in sperm cells leading to infertility cases, hemospermia (abnormal pink or reddish coloured seminal fluid) which could be due to inflammation, infection, blockage or injury of the male reproductive tract such as the urethra, testicles, epididymis or prostate etc and also to detect infections related to STDs like HIV, HPV etc, post-vasectomy confirmation, Semen cryopreservation – preservation of semen for IVF etc. A culture and sensitivity test in semen aims at detecting potential pathogenic microbes (such as UTI, STD etc) that may cause infection of the male genitor-urinary tract to prevent further complications such as male infertility (i.e it can cause impaired spermatogenesis –eg. Oligospermia and in long term can lead to sterility in the male). Sperm bacterial (eg. E. coli, Staphylococcus etc interferes with semen quality, activity, agglutination of the sperms, decreases sperm concentration, motility, morphology, vitality, etc of the sperm) contamination is quite frequent and could contribute to the deterioration of the sperm quality of infertile men and also early detection can protect from conditions like prostatitis –infection causing inflammation of the prostate gland. Clinical signs and symptoms of prostatitis include pelvic pain, urinary tract symptoms, dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary retention, fever, chills, nausea, emesis, malaise etc. Gram Stain Test: This test checks for the presence of harmful pathogenic microbes in suspected infection, for example in the throat, lungs, skin wounds, genitals etc and moreover in body fluids such as blood, urine etc. The two main categories of bacterial infections are gram-positive and gram-negative. This screening for diagnosis is done by the differentiation made, based on how the bacteria react to the gram stain. A gram stain is coloured purple and if the bacteria remain in purple colour it is gram-positive bacteria and incases the bacteria turns red or pink they are gram-negative bacteria. Examples of gram-positive bacteria include nosocomial infection caused by methicillin-resistant Streptococcus aureus (MRSA), Strep infections, toxic shock etc. Examples of gram-negative infections include Salmonella, pneumonia, gonorrhea, UTI etc. The significance of differentiating the nature of bacteria as gram-positive or gram-negative helps the physician to begin the most effective antibiotic therapy for treating it. If the test result shows the presence of more than (≥15) colonies along with the same organism isolated from peripheral blood along with clinical signs and symptoms, then the case is said to be an infected positive case. Other gram stain tests include the Acid Fast Test (eg. For mycobacterium causing TB etc). Clinical manifestations include chills, fever, fatigue, nausea, confusion, increased heart rate, nasal flare due to increased breathing -which may or may not be associated with shortness of breath on physical exertion, inflammation (presenting with cardinal signs of inflammation like – rubor, tumor, calor, dolor and loss of function), blood clots, drop in blood pressure, organ failure, elevated WBCs etc. Once tested positive, then the additional supportive tests are ordered for - Evidence-Based Therapy (EBT) such as CBC, test for the presence of bacterial toxins (release of toxic by-products) eg staphylococcal infection, in case of foodborne-illness/food poison (or their toxins), different sample specimen collected for tests eg. blood, stool, urine culture, sputum test, CSF sampling, ascetic fluid, pleural fluid, pericardial fluid, synovial fluid, complement test (to check for increased levels of C3) etc. Moreover, sensitivity tests (also known as susceptibility testing) are also performed for appropriate antibiotic treatment & for better prognosis eg. MRSA – Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, VMSA Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus etc. Other tests other than culture and sensitivity of semen for the source of infection includes microscopic examination and evaluation of semen analysis, blood tests like CBC, differential WBC count (in case of infection), Prostate-Specific Antigen test, testosterone, FSH, ELISA test for Mumps antibodies etc, other hormonal assays eg. pituitary hormones (in case of tumours etc), urinalysis to check for UTI, digital rectal examination to confirm pain and swelling of the prostate, CT Scan, ultrasound (vericocele), genetic tests like DNA etc.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - semen. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centres to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



