Culture & Sensitivity –Pus:
Why Culture and Sensitivity – Pus Specimen Test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
Skin is the largest organ present in the human body. It serves as an anatomical barrier between sterile internal organs and the external environment (pathogenic microbes). A breach in the skin or mucosal surface (eg. bites, trauma, surgery, or diseases) may result in skin or soft tissue infections that may spread around or eventually to other parts of the body if untreated. Pus is a natural part of the healing process of suppurating wounds. Pus is a sign of an infected wound and the body’s defense mechanism (immune system) fights against the invading infection and healing the injury (wound healing). Pus is a thick, foul odor and usually yellowish or greenish (color depends on the location and type of infection) opaque fluid (protein-rich fluid: Puris) produced in the infected site of the tissue which contains a collection of infectious dead microbes, dead WBCs, tissue debris like remains of dead cells – infected host cells and serum, etc. Complications of un-drained pus include skin abscess, fistula (abnormal communication between two parts such as organs, blood vessels, and another structure eg. blind type and/or complete type of fistula), the spread of infection to the surrounding areas (invasive spread), recurrence of infection, systemic infection, sepsis, etc. Examples of pyogenic bacteria include Staphylococcus species, E Coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhea, Actinomyces, Burkholderia mallei, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc. Fungal infections include tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), Histoplasma, candida, actinomycetes, etc that can cause from site of wound infection to dispersive type known as mycotic mycetoma. Complications due to prolonged pyogenic infections can lead to impetigo (usually in children), osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, necrotizing fasciitis, etc. Clinical manifestations of an infected wound include signs of inflammation (rubor – redness, tumor – swelling, calor – heat, dolor – pain, and loss of function), pus or bad-smelling /odorless fluid drain from the wound, boils, rashes, pustules, etc and in case of systemic manifestation it shows the signs and symptoms of fever, fatigue, chills, confusion, etc. Culture and Sensitivity test in Pus Specimen facilitates the treatment of wound infection. This test helps to determine if a wound is infected (presence of the pathogenic organism in positive culture results shows an infected wound), to reveal the type of infection (eg. bacterial – aerobic in case of open wound or anaerobic bacteria in case of punctured closed wound, gram-positive or gram-negative strains – based on the presence of cell wall, fungal infection, etc) and to establish best possible medication to treat the infection – susceptibility testing (A clear circular holo known as plaque or zone of inhibition (antibiotic has inhibited the growth or killed the colonies of harmful pathogens) appears around the antibiotic disc indicates the absence of bacteria). This helps in the discrimination of type of antibiotic treatment such as broad-spectrum / narrow-spectrum antibiotics to heal the wound (in case of bacterial resistance to antibiotics, if no discernable plaque/zone of inhibition is found around filter paper with antibiotic hence effective medication is prescribed). If the culture result is negative it shows a sterile wound (free from pathogenic microbes). This pus swab culture and sensitivity test are ordered in cases of conditions such as patients with delayed wound healing, risk of spread of infection to the surrounding areas causing secondary complications affecting another organ (s) or organ systems, allergies, causing systemic manifestations, co-morbid and/or underlying medical conditions like diabetes, hypertension, vascular diseases like DVT, sepsis, etc and to avoid further complications. Other tests include blood tests to check CBC, use of Mass Spectrometry using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight – MALDI-TOF to identify and confirm the genus and species of a bacterial colony grown on culture medium within half an hour, tests for fungal infection, liver function, blood sugar and proteins (antibodies using ELISA), urine tests, aspiration fluid (ascites) or tissue biopsy in deeper wounds (fungal spores, etc) or sample specimen (sputum, blood, urine, etc) collected from other suspected sites (bone marrow specimen in osteomyelits etc) for histopathological studies, PCR, etc.
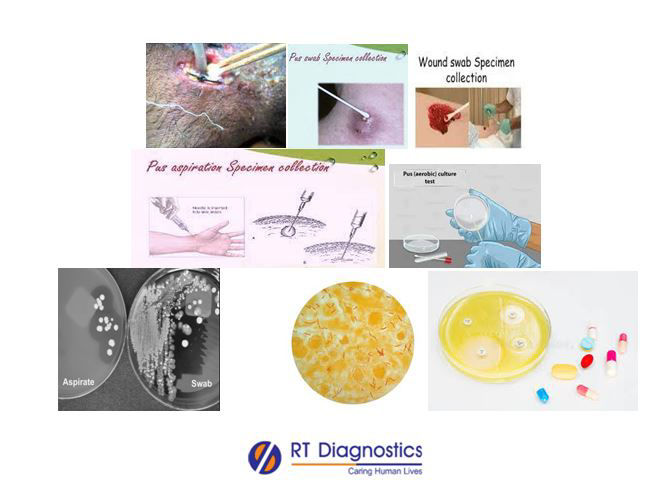
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen – As directed by the physician or the pathologist Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
Sample Requirement: As directed by the physician or the pathologist Test Preparation: None
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



