Cervical region
Why Cervical region Test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
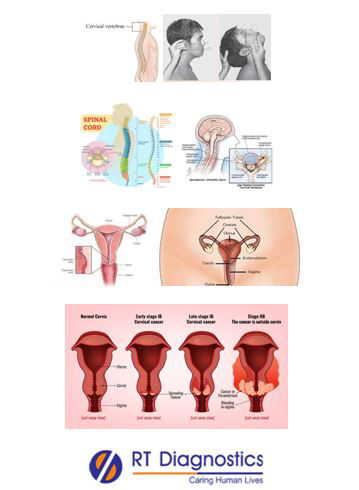
The medical term cervical is related to the neck or to the neck of any organ or structure. Cervical lymph nodes are located in the neck. Common symptoms of Cervical spondylosis are neck pain or stiffness, nagging soreness in the neck, muscle spasm, popping or grinding sound on movement, dizziness, headaches etc. Complications of cervical spondylosis may present with anatomical and functional adaptive changes in the brain, since prolonged chronic condition may lead to damage of white matter, grey matter volume loss and functional adaptive changes in the sensori-motor cortex etc.
Some of the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the neck include sharp pain in the arm, radiating pain in the shoulder, numbness or pins and needles sensation, weakness of the arm, worsening of pain on movement of the neck along with the head. Moreover cervical refers to the cancer of the uterine cervix, which is the lower, narrow end (the neck) of the uterus. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus located at the end of the vagina (a cylinder-shaped structure that connects the vagina and the uterus). After an abnormality has been found during a routine Pap smear (colposcopy-a special way of looking at the cervix using light and a low-powered – compound microscope to make the cervix appear much larger) or pelvic examination (diagnostic evaluation), the gynecologist may order for a cervical biopsy. Hence Cervical region test remains an important Clinical Assessment method by physicians (Obstetrics and Gynaecologist) for diagnostics based on the patient’s signs and symptoms. Moreover, Cervical biopsy is a minor surgical procedure (as a part of the assessment – in which a small amount of tissue is removed from the cervix) that may be performed to confirm pre-cancerous (cells that appear to be abnormal, but not yet turned cancerous – are first signs of cancer, that may develop years later) cells on the cervix. Gynecologists may also perform a cervical biopsy to diagnose or treat certain conditions such as genital warts or polyps (non-cancerous growth of the cervix). Risk factors for developing cervical cancer are human papilloma virus - HPV (DNA test for HPV is performed for confirmation). Types of cervical biopsies are punch biopsy, cone biopsy (conization), electric wire loop, and endo-cervical curettage. Symptoms of cervical cancer – vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse, irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, or abnormal vaginal discharge like white discharge, etc. Possible complications of cone biopsies include bleeding, infection vaginal tears, cervical stenosis due to scarring (causes impaired menstrual flow), narrowing of the cervix, and infertility. Conditions that may interfere and give less accurate results are menstruation, acute (active) pelvic inflammatory diseases, and acute inflammation of the cervix. Do’s and dont's before the test – Do’s are empty the bladder and bowel before the test, and dont's are do-not douche, do-not place any products in the vagina, do-not have inter-course for 24 hours before the test examination is performed. Other tests include examination of bladder and rectum, imaging tests such as CT scan, MRI, or Ultrasound.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Blood sample collected from the vein/specimen as suggested by the physician. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
Sample Requirement: blood sample / Tissue from the Cervix/specimen sample as guided by the physician
Test Preparation: None
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



