ALBUMIN – ASCITIC FLUID:
CLINICALINFORMATION
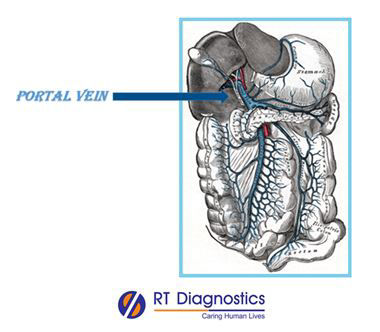
Albumin Ascitic fluid is necessary for the assessment of portal hypertension. The serum ascites albumin gradient (SAAG) is necessary to determine if the patient’s ascites are caused due to portal hypertension (reflecting underlying pathology in the liver’s portal vein). The calculation of SAAG is performed by measuring both the serum albumin and ascetic fluid albumin concentrations and subtracting ascetic fluid albumin from the serum albumin. This determines to classify transudate from exudate (reflecting the cause of pathology i.e. altered physiology from infectious cause).
Portal hypertension develops when resistance to portal blood flow increases. There is an increase in the pressure within the portal vein which carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver. The most common cause is thrombosis (clot), cirrhosis of the liver, etc. the symptoms and complications of portal hypertension include gastrointestinal bleeding (black, tarry stools, or blood in stools), esophageal varices (vomiting of blood due to rupture and hemorrhage from varices), ascites (an accumulation of fluid in the abdomen), etc. The causes of portal hypertension are classified into three as pre hepatic, hepatic, and post hepatic conditions. The resistance to the portal blood flow increases due to portal vein thrombosis, splenic vein thrombosis stenosis of the portal vein, arterio-venous fistula with a thrill – palpable murmur ie. Fusion created artificially due to iatrogenic cause (pre-hepatic causes), cirrhosis due to alcohol, biliary atresia, biliary cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, granulomatous or infiltrative liver disease such as sarcoidosis, lymph proliferative malignancies amyloidosis, Gaucher’s disease, fatty liver disease, viral hepatitis, etc. (hepatic causes) and constrictive pericarditis (right-sided heart failure), Budd-Chiari syndrome(also called hepatic vein thrombosis), inferior vena cave obstruction (post-hepatic causes). The signs of portal hypertension are usually gastrointestinal hemorrhage reflected in the stool (lower GIT) or vomit (upper GIT). Those patients with more advanced liver disease often present with ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, jaundice, coagulopathy, or spider angiomata. Signs and symptoms of portal hypertension are ascites (free fluid accumulation in the peritoneal cavity), abdominal tenderness (spontaneous bacterial peritonitis), and splenomegaly leading to fewer platelets (thrombocytopenia), anorectal varices, a swollen vein in the anterior abdominal wall (caput-medusae).
General instructions:
Sample Requirement: specimen – Ascitic fluid from the abdominal cavity. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presentingcomplaints / signs or symptoms:
SPECIMENREQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory “RTDIAGNOSTICS” provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



