ALBERT – STAIN (Swab) :
CLINICAL INFORMATION :
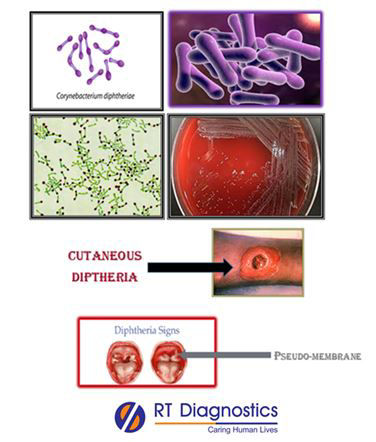
Albert’s staining technique is a type of special staining technique used to demonstrate the bacterial structure under a microscope. It specifically demonstrates the meta-chromatic granules found in Corynebacterium diphtheria that causes diphtheria. Albert’s stain consist of two (basic dyes) components namely toluidine blue “O” and malachite green which has a high affinity for acidic tissue components like meta-chromatic granules present in the cytoplasm of the bacteria Corynebacterium diphtheria. It infects the nasopharynx or skin. These toxigenic strains secrete a potent exotoxin which causes diphtheria. This exotoxin of Corynebacterium diphtheria bacteria gets absorbed in the blood which in turn damages heart, kidney, and nerve cells by blocking protein synthesis. The symptoms of diphtheria include pharyngitis, fever, swelling of the neck or area surrounding the skin lesion. The classical sign is the lesion covered by a grey pseudo-membrane (consists of fibrin, Corynebacterium diphtheria bacteria, and inflammatory cells), which on breaching bleeds.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: specimen - swab throat. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presentingcomplaints / signs or symptoms:
SPECIMENREQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory “RTDIAGNOSTICS” provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



