ADA - Ascitic Fluid
ADA (adenosine deaminase)is an enzyme that involves in the metabolism of Purine. It breakdowns the Adenosine present in the food we consume and that precursor is used to convert into nucleic acid synthesis for the body. ADA plays a vital role in regulating the Immune System of the body. ADA levels are used to diagnose Tuberculosis in various places. ADA levels in Ascitic Fluid helps to detect Peritoneal Tuberculosis. Other tests performed are clinically for ascetic fluid are by inspection for bulging flanks, auscultation. Followed by clinical examination by palpation, flank dullness, shifting dullness, etc for performing ascetic tap.
ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (ADA) - ASCITIC FLUID:
CLINICAL INFORMATION :
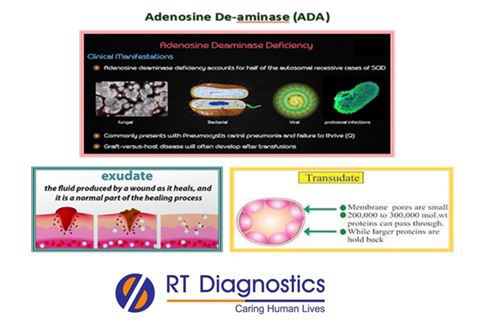
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) levels in Ascitic fluid is a potential marker for the diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) in the peritoneum caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis leading to an infection known as tuberculous peritonitis. Adenosine deaminase also known as adenosine aminohydrolase or ADA is an enzyme involved in purine metabolism. This enzyme is needed for the breakdown of adenosine from the food and for the turn-over of nucleic acids in tissues. ADA-1 is an intracellular enzyme protein, while ADA-2 is an extracellular enzyme protein highly expressed by myeloid immune cells such as monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells. The function of ADA is to catalyze adenosine (it is one of the four nucleosides which is a building block for DNA and RNA) and also serves as a growth factor (hence the treatment of ADA is TNF inhibitors which reduces vasculitis), moreover ADA functions as intracellular DNA sensor. The most important primary function of this enzyme is in the development and maintenance of the immune system (deficiency of ADA causes pulmonary inflammation, thymic cell death, defective T-cell receptor signaling, and also severe combined immune deficiency - SCID) and its other functions include epithelial cell differentiation, neurotransmission, gestation maintenance and stimulates the release of excitatory amino acids. ADA is also increased in many diseases particularly those associated with the immune system, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and sarcoidosis. Low levels of ADA lead to pulmonary fibrosis whereas chronic exposure to high levels of ADA leads to exacerbating inflammation instead of suppressing them. The estimation of enzyme adenosine deaminase is performed as a marker for the diagnosis of TB since this enzyme level is increased due to the stimulation of T-cell lymphocytes by mycobacterial antigens. Test on the ascetic fluid is performed to differentiate between transudates (it is a filtrate of blood caused due to increased pressure in veins and capillaries that forces fluid through vessel walls or to a low level of protein in blood serum and since transudate accumulates in tissue outside the blood vessels hence causes edema) and exudates (the fluid that filters from the circulatory system into lesion or areas of inflammation which is usually comprised of serum, fibrin, and leucocytes). This differentiation is based on fluid albumin level i.e. the serum-ascites albumin gradient (SAAG) calculation, which is serum albumin level minus the fluid albumin level will distinguish if it is a case of exudate or transudate. Some of the complications of ascites include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (a life-threatening infection of the ascetic fluid), kidney failure (hepato-renal syndrome), hepatic encephalopathy (COMA), mental confusion, change in the level of alertness, weight loss, and protein malnutrition, etc. The differential diagnosis for peritoneal tuberculosis can mimic malignancy in women since the female ascites specimen usually have elevated levels of CA125 levels. In children symptoms of ADA deficiency are pneumonia, chronic diarrhea, widespread rashes, developmental delay, and also with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) characterized by disturbed development of functional T-cell and B-cell.
Other tests include enzymatic assays or colorimetric, HPLC, spectrophotometry, etc.
General instructions:
Sample Requirement: specimen - aspiration from the local site - Ascitic Fluid collected from Peritoneum. Test Preparation: none.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presentingcomplaints / signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory “RTDIAGNOSTICS” provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



