Acid Phosphatase (With Prostatic Fraction)
Acid Phosphatase is an enzyme found in the liver, bone marrow, and prostate gland. This test measures to quantify the enzyme phosphatase in the blood. The excess level of that enzyme is a sign of prostate cancer, prostate hypertrophy, and its associated infections. This test helps to diagnose metastasis of prostatic carcinoma.
ACID PHOSPHATASE (Fraction):
CLINICAL INFORMATION :
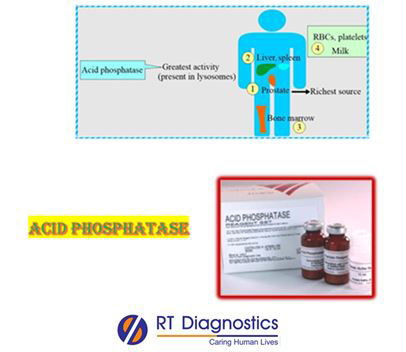
Acid phosphatase is a ubiquitous lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyses organic phosphates at an acid pH. This enzyme is present primarily in the bone, prostate, platelets, erythrocytes, and spleen. Abnormally high serum levels of acid phosphatase may indicate infection, injury, or cancer of the prostate (hence confirmation is done by prostate-specific antigen test - PSA).
The fractional acid phosphatase test is also called Tartarate-labile prostatic phosphatase (PAP). Acid phosphatase is an iso-enzyme and hence the fractionation test is recommended as a routine screening test for those patients whose serum acid phosphatase is abnormally high, since not only the test indicates the presence or absence of prostatic cancer but also it helpful in screening for the diagnosis if there is bony metastasis or not.
General instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Blood sample drawn from the vein. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presentingcomplaints / signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory “RTDIAGNOSTICS” provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



